An IoT-Enabled, THD-Based Fault Detection and Predictive Maintenance Framework for Solar PV Systems in Harsh Climates: Integrating DFT and Machine Learning for Enhanced Performance and Resilience
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.63318/waujpasv4i1_05Keywords:
Energy management system, Fault Detection, Fast Fourier transform, Real-Time monitoring, Machine learningAbstract
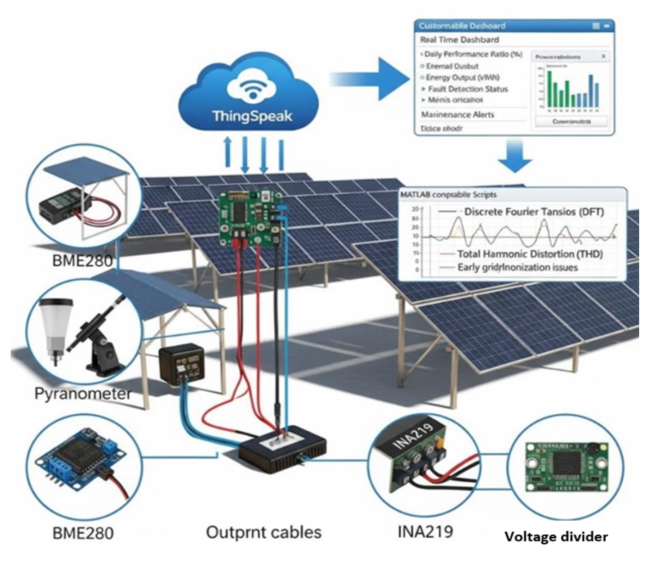
This research introduces an advanced energy management approach for PV setups situated in demanding semi-arid environments, specifically focusing on Baniwalid, Libya. Conventional energy management systems often depend on fixed parameters or basic models, which only address a limited scope of environmental variables. Such systems lack the adaptability to effectively respond to fluctuating conditions like intense heat, dust buildup, and intermittent shading, all of which can undermine solar panel performance. To overcome these limitations, the study incorporates artificial neural networks within an Internet of Things-based framework. This system utilizes a network of affordable sensors to collect real-time operational data from PV arrays. Via applying Discrete Fourier Transform techy, the system extracts key features such as Total Harmonic Distortion from electrical signals, which serve as early indicators of potential faults. Machine learning algorithms then leverage this data to forecast energy output as well as monitor the daily performance ratio, enabling the detection of gradual performance declines. During a ten-day observation period, the framework recorded a decrease in DPR from 97% to 93%, primarily attributed to temperature swings as well as dust accumulation on solar modules. The ANN-based model successfully correlated predicted outcomes with actual measurements, highlighting its potential for accurate system health assessment. The hybrid methodology combining physics-based signal analysis with data-driven intelligence facilitates proactive maintenance strategies that minimize unexpected interruptions, optimize energy yields, and can be efficiently deployed at the network edge. By transforming PV systems into adaptive, self-monitoring assets, this work enhances operational resilience under extreme conditions and offers a scalable solution that can be applied to smart energy management globally.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This journal uses Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommerical 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
Copyright of articles
Authors retain copyright of their articles published in this journal.




