Association between Blood Glucose Levels and Biochemical Variables in COVID-19 Patients - A Cross-Sectional Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.63318/waujpasv4i1_07Keywords:
Blood glucose, COVID-19, Insulin, PatientsAbstract
Objectives: To identify the association between blood glucose concentrations and biochemical variables that lead to high blood glucose levels in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
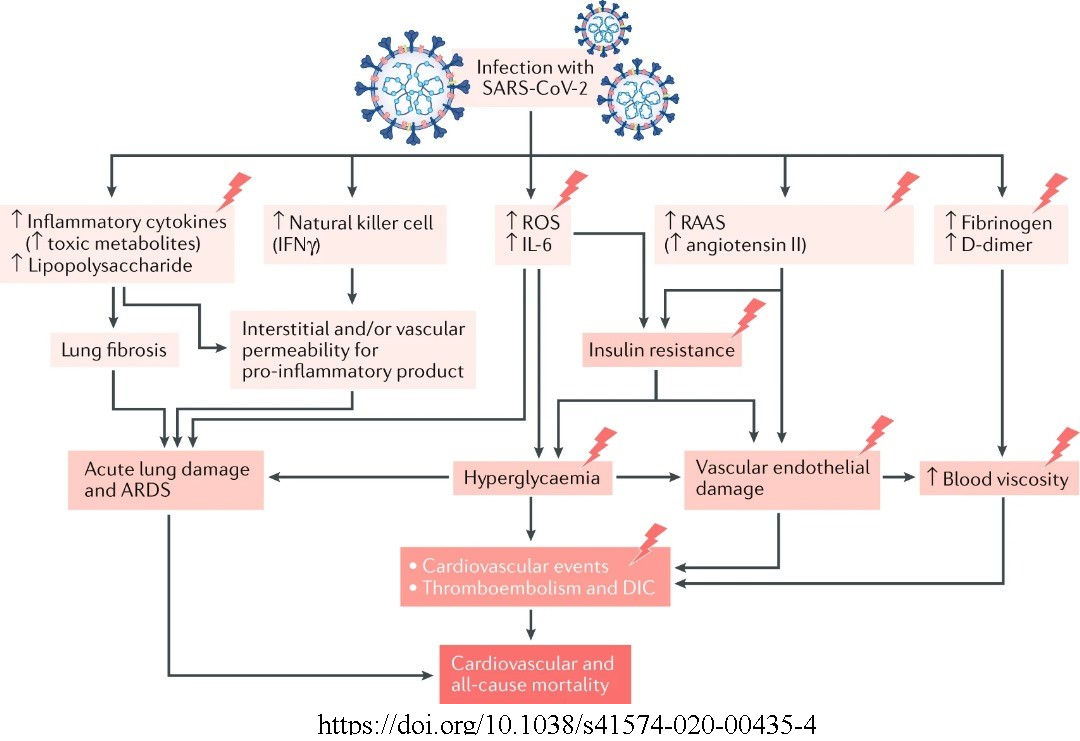
Methods: This study was conducted on 100 plasma samples obtained from individuals with confirmed COVID-19, diagnosed using polymerase chain reaction. Samples were collected from the Barakuli Isolation Centre, Respiratory Clinic, and Sebha Medical Center in Sebha City, Libya. Concentrations of glucose, insulin, cortisol, triglycerides, cholesterol, C-reactive protein, and liver enzyme activities were measured.
Results: Sixty percent of patients had elevated blood glucose concentrations, whereas 40% had normal concentrations. The levels of insulin, cortisol, CRP, triglycerides, and liver enzyme activity were compared between the two groups. The results showed an increase in the mean concentrations of cortisol, triglycerides, CRP, and liver enzymes in patients with elevated glucose concentrations compared with those in patients with normal glucose concentrations. Statistical analysis using the t-test showed significant differences between the means (p = 0.000). Conversely, the mean insulin concentration was low in patients with elevated glucose levels. The results also showed a positive correlation between glucose and cortisol, triglyceride, and CRP concentrations, as well as GPT and GOT activity.
Conclusion: Patients with COVID-19 exhibited elevated blood glucose concentrations associated with decreased insulin levels. Additionally, high concentrations of biochemical variables contributing to hyperglycemia were observed in patients with COVID-19.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This journal uses Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommerical 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. To view a copy of this license, visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
Copyright of articles
Authors retain copyright of their articles published in this journal.




